Co-authored-by: pejour <pejour@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Damien Guillotin <damguillotin@gmail.com>
5.2 KiB
BE PI3D : MVS par level set
Usefull resources
Level set method, Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Level-set_method
Level set, Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Level_set
TP3, Stéréoscopie multi-vues (MVS)
https://moodle-n7.inp-toulouse.fr/pluginfile.php/116746/mod_resource/content/2/sujet_TP3.pdf
Coding Adventure: Terraforming, Sebastian Lague
3D Signed Distance function (NVIDIA Research)
2022 Towaki Takikawa Andrew Glassner Morgan McGuire
https://tovacinni.github.io/sdf-explorer/
A GPU Implementation of Level Set Multiview Stereo
2006 Patrick Labatut Renaud Keriven Jean-Philippe Pons
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/11758549_33 https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/11758549_33.pdf?pdf=inline%20link
Fast Level Set Multi-View Stereo on Graphics Hardware
2006 Patrick Labatut Renaud Keriven Jean-Philippe Pons
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4155801 https://sci-hub.hkvisa.net/10.1109/3dpvt.2006.62
Model-based multiview stereo via level sets with statistical shape prior
2011 Moumen El-Melegy Nagi Al-Ashwal Aly A. Farag
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6365368 https://sci-hub.hkvisa.net/https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6365368
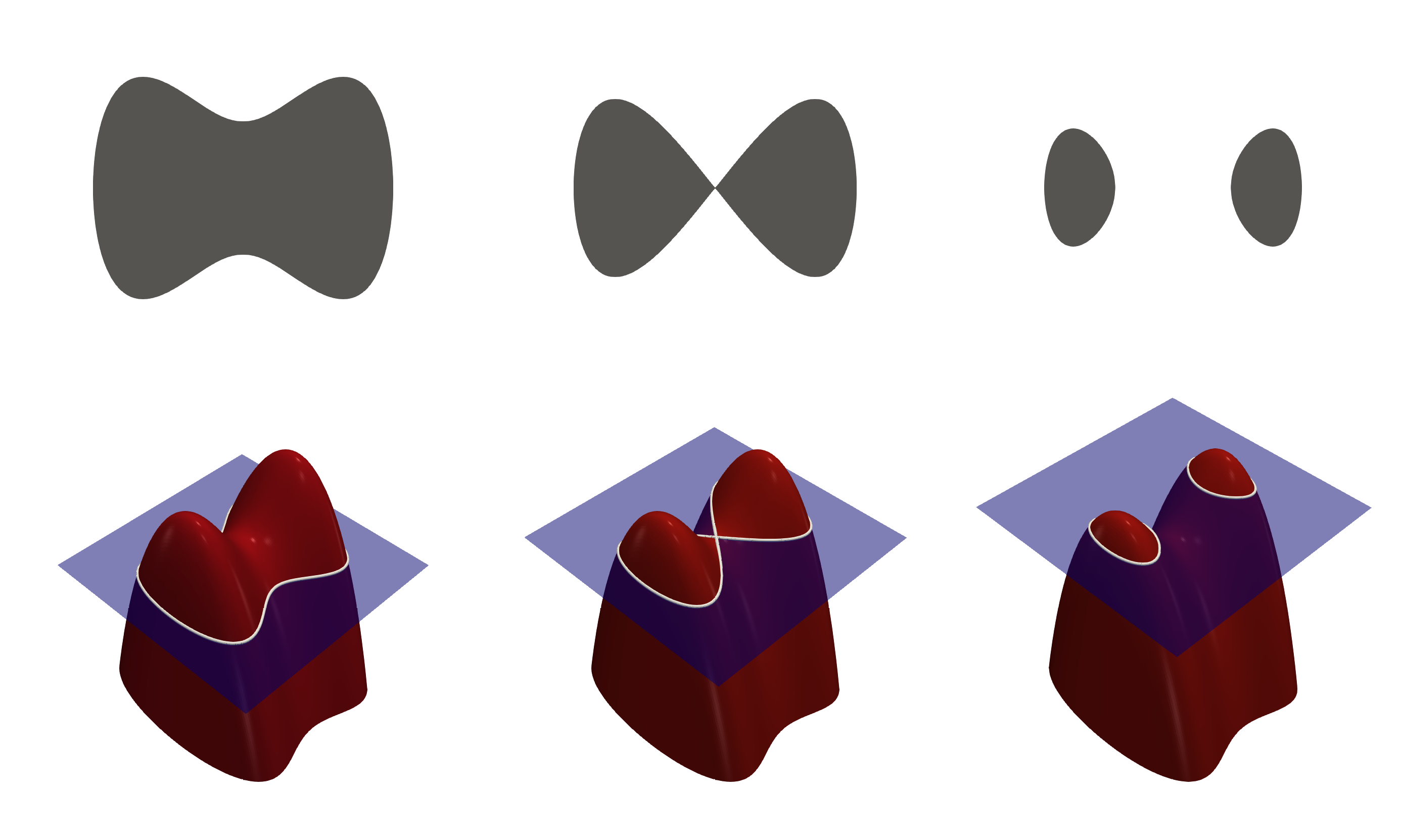
Équation bizarre de l'idée générale
g(x,y)=exp(-((0.2*x)^(2)+((y^(2))/(x^(2)+0.1))))*sig(-10*x)-5*exp(-((y^(2))/((0.1*x)^(2))))*sig(10*x)
g(x,y) = \exp\left(-\left(\left(0.2x\right)^2 + \left(\frac{y^2}{x^2 + 0.1}\right)\right)\right)\sigma\left(-10x\right) - 5\exp\left(-\frac{y^2}{\left(0.1x\right)^2}\right)\sigma\left(10x\right)A Level-Set Approach to 3D Reconstruction from Range Data
1998 Ross T. Whitaker
https://www.cs.utah.edu/~whitaker/sceneRecon/papers/sparse_report.pdf https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/A:1008036829907 https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1023/A:1008036829907.pdf?pdf=button
Level Set Methods in Computer Vision (Slides)
2006 Daniel Cremers Department of Computer Science University of Bonn
https://www.csd.uwo.ca/~yboykov/Presentations/ECCV06_tutorial_partII_dan.pdf
On part d'un solide qu'on rogne en soustrayant les valeurs obtenues avec les gaussiennes => jusqu'à obtenir le solide étudié.
Variational principles, surface evolution, PDEs, level set methods, and the stereo problem
1996/1998 Olivier Faugeras Renaud Keriven
https://hal.inria.fr/inria-00073673/document https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/661183
Multi-View Stereo: A Tutorial
2015 Yasutaka Furukawa Carlos Hernández
https://carlos-hernandez.org/papers/fnt_mvs_2015.pdf
amy-tabb/tabb-level-set-segmentation
https://github.com/amy-tabb/tabb-level-set-segmentation
Ramesh-X/Level-Set
https://github.com/Ramesh-X/Level-Set
3D Image Reconstruction and Level Set Methods
Introduction and derivation of the level set methods.
https://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=3811&context=etd
J. A. Sethian, Level set methods and fast marching methods - evolving interfaces in computational geometry, fluid mechanics, computer vision, and materials science (1999)
https://math.berkeley.edu/~sethian/2006/level_set.html
Les bons tuyaux de Lilian
Voici les références pour le groupe de BE de Laurant, des références pour lesquelles la reconstruction 3D sont les zeros d'un level set (entre parenthèses : la nature de la fonction dont les paramètres sont optimisés) :
- IDR (fonction de distance signée) : Multiview Neural Surface Reconstruction by Disentangling Geometry and Appearance
- Neus (fonction de distance signée) : NeuS: Learning Neural Implicit Surfaces by Volume Rendering for Multi-view Reconstruction
- Unisurf (fonction d'occupation, terme traduit de l'anglais occupancy) : UNISURF, Unifying Neural Implicit Surfaces and Radiance Fields for Multi-View Reconstruction
- VolSDF (fonction de distance signée) : Volume rendering of neural implicit surfaces Les quatre méthodes font du rendu dit surfacique, les trois dernières (Neus, Unisurf and VolSDF) étant "hybrides", à savoir utilisant du rendu surfacique et volumique. N'hésitez pas à nous demander plus d'informations si besoin. Une autre référence avec un mélange de MVS et de PS qui considère le niveau d'incertitude des deux méthodes respectivement pour utiliser en chaque pixel le résultat le plus fiable (level set et equation eikonale dans leur fonction de cout) : https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2022/html/Kaya_Uncertainty-Aware_Deep_Multi-View_Photometric_Stereo_CVPR_2022_paper.html
Un autre article à lire :
https://hal.inria.fr/inria-00266287/file/GargalloPradosSturm-iccv2007.pdf
A Fast Voxel Traversal Algorithm for Ray Tracing :
http://www.cse.yorku.ca/~amana/research/grid.pdf https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NbSee-XM7WA
Note
Eviter papier de BOYKOV CREMERS
A demander
Quel estla différence avec la méthode vu en TP ?
- On calcule le MVS comme d'hab -> Carte de profondeur par image
- Pas de projection en nuage de points dense -> Utilisation de la carte de prof pour modifier le level set initiale ?